Another vulnerability has sprung up you should pay attention to as you need to make some changes to your web browser of choice likely.
Read the link below
Health Infosec web site
Basically you should disable support for SSLv3 and the specifics for most browsers are below.
Additionally if you run a web server or services, you should take a look also. There are
links at the bottom to test both your browser and server.
It really requires a MITM (Man in the middle) type attack, so you are more at risk than others
if you are someone who uses guest wireless networks that are not encrypted. (like some free
wifi hotspots, etc). My suggestion would be to simply mitigate the risk and disable it and then
make adjustments if you find it breaks something you need.
Firefox specific info
Mozilla Posting of info
Fix Firefox (click on images to see larger example)
Open the browser then type “About:config” (without the quotes) in address bar – it will warn you about breaking things,
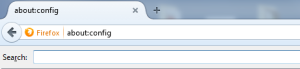
then search for
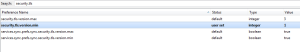
Security.tls.version.min
Change setting from 0 to 1
Mozilla says they are fixing this permanently in Version 34 being releaed in November.
The test below may show you are not vulnerable, but you likely are and should change this setting unless you don’t feel the need. I have seen a false positive (meaning I am safe) but I clearly was not.
Fix Google Chrome specific info
Google Blog Info
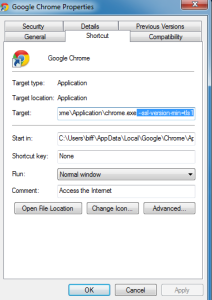
Disable SSLv3 by putting the command below at the end of your chrome launch command (Windows example below – typically right click the icon and go to properties then shortcut)
–ssl-version-min=tls1
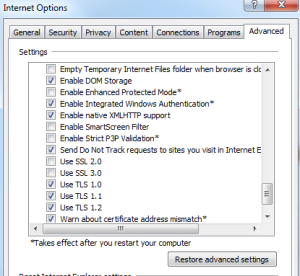
Fix Internet Explorer specific info
Go to Internet Options / Advanced after you start the browser and uncheck use SSLv3 if checked.
Microsoft technet link discussing various options and steps including server admin info
Microsoft Technet info
++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
Browser Poodle test
https://www.poodletest.com/
Server test
https://www.ssllabs.com/ssltest/analyze.html
 EMET or Enhanced Mitigation Experience Toolkit (someone in marketing needs fired) is an MS tool that adds some protections against attacks. It provides some advanced functionality.
EMET or Enhanced Mitigation Experience Toolkit (someone in marketing needs fired) is an MS tool that adds some protections against attacks. It provides some advanced functionality.